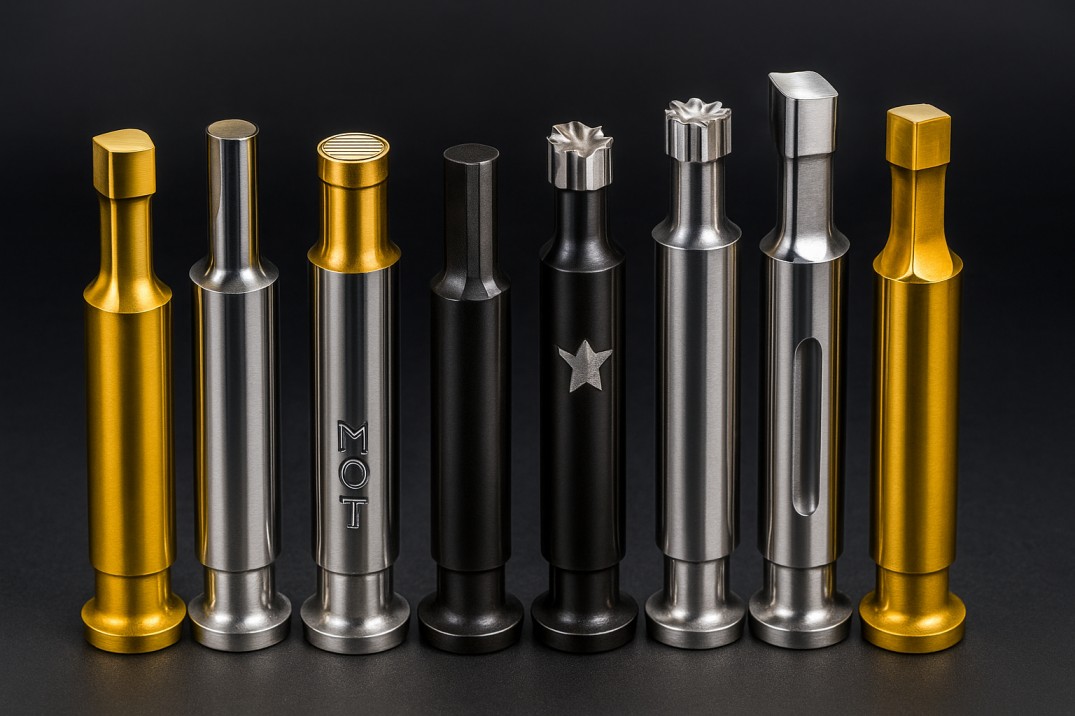
If you work with pharmaceutical tablet presses, you know that punches and dies take a beating. Over time, a brand-new set of tooling can turn into a source of headaches – sticking granule residue, worn punch tips, rust spots, or even cracked tooling. The good news is that you can dramatically extend the life and performance of tablet press tools by applying the right surface coatings.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the best tool coatings for tablet presses – from old standbys like hard chrome plating to advanced PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) films like titanium nitride (TiN) and chromium nitride (CrN). Whether you’re a pharmaceutical engineer solving production snags or an industrial procurement manager comparing tooling options, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision.
Why Tablet Press Tooling Needs Coatings
Why do tablet press tools need special coatings? In a word: performance. Tablet compression is a high-pressure, high-friction process. The uncoated steel surface of punches can react with formulations, leading to:
- Sticking (powder adhering to punch faces)
- Picking (logos getting pulled off onto punches)
- Wear and abrasion (dulling of punch edges, die bore wear)
- Corrosion (rusting from moisture or reactive ingredients)
Coatings act as protective armor – they harden the surface, reduce friction, and create a non-reactive barrier. The FDA’s regulations for equipment (21 CFR 211.65) require that all contact surfaces are non-reactive and won’t alter the drug product. A well-chosen coating ensures compliance by preventing metal contamination and chemical reactions between the product and the tooling.
The right punch and die coating can extend tooling life by up to 10x, reduce downtime for cleaning, and ensure smoother tablet production. Let’s break down the top coating options, their pros and cons, and how to choose the optimal coating for your specific tablet formulations.
Coating Comparison Overview
| Coating Type | Hardness (HV) | Color | Primary Benefit | Best For | Cost Level | Wear Life Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Chrome (HCP) | 800-900 | Silver/Mirror | Basic protection | General use, budget applications | Low | 2x |
| Electroless Nickel (ENi) | 500-1000* | Silver/Matte | Uniform smoothness | Sticky formulations, corrosion | Low-Medium | 2-3x |
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | 2300 | Gold | Maximum hardness | Abrasive wear, visibility | Medium | 5-10x |
| Chromium Nitride (CrN) | 2000-2500 | Silver-Gray | Anti-stick performance | Sticking/picking issues | Medium | 5-10x |
| Multi-Layer CrN (MCrN) | 2000-2500 | Silver-Black | Ultimate durability | Extreme conditions | High | 10x+ |
| PVD Chrome | 1200-1800 | Silver | Ultra-smooth surface | Severe sticking problems | High | 5-8x |
*With heat treatment
Quick Selection Guide
Choose Hard Chrome if: Budget is primary concern, basic protection needed Choose Electroless Nickel if: Dealing with sticky formulations or corrosive ingredients
Choose TiN if: Wear resistance is top priority, want visual wear indication Choose CrN if: Sticking is the main problem, need balanced performance Choose MCrN if: Operating under extreme conditions, maximum durability required Choose PVD Chrome if: Standard coatings haven’t solved sticking issues
Hard Chrome Plating (HCP)
Description: Hard chrome plating is a traditional electroplating process where a layer of chromium metal is deposited on the punch or die. It’s been used for decades in tablet tooling and has a shiny, reflective silver appearance.
Advantages
Hard chrome became popular because it offers good basic protection on multiple fronts:
- Increased hardness – Chrome plating can roughly double the lifespan of a standard steel punch by reducing wear
- Lubricity – Chromed surfaces feel slicker, helping tablets release easier
- Corrosion resistance – Shields steel from moisture and many chemicals
- Cost-effective – Widely available and relatively inexpensive
Drawbacks
Despite its historical use, hard chrome has significant downsides compared to modern coatings:
- Micro-cracks – The plating process creates tiny cracks that expose underlying steel to corrosion
- Hydrogen embrittlement – Can reduce tool strength by up to 20% due to hydrogen absorption during plating
- Environmental concerns – Uses toxic hexavalent chromium baths that are heavily regulated
- Limited hardness – At ~900 HV, it’s only half as hard as modern PVD coatings like CrN (~2000 HV)
Best Uses
Hard chrome plating is still used as a cost-effective general-purpose coating for stable formulations without severe sticking or abrasion issues. It’s commonly applied on tablet press turrets and cam tracks, and remains popular for budget-conscious operations.
Electroless Nickel Plating (ENi)
Description: Electroless nickel plating is a chemical deposition method where a nickel-phosphorus alloy is deposited uniformly without electrical current. Often enhanced with PTFE (Teflon) for anti-stick properties.
Advantages
The key advantages include:
- Uniform coating – Plates evenly across complex shapes, including inside engravings
- Ultra-smooth finish – Lower surface roughness than base steel reduces mechanical sticking
- Excellent corrosion resistance – Nickel-phosphorus alloys resist chemical attack
- No hydrogen embrittlement – Chemical process avoids electrical current issues
- Anti-stick properties – Especially effective when combined with PTFE
Performance Characteristics
- Hardness: 500-600 HV as deposited; up to 850-1000 HV after heat treatment
- Surface finish: Exceptionally smooth, mirror-like appearance
- Friction: Very low, especially with PTFE incorporation
Drawbacks
- Lower hardness than PVD coatings – May wear faster in highly abrasive applications
- PTFE wear – The Teflon component gradually wears away, requiring recoating
- Nickel concerns – Some companies avoid nickel on product surfaces due to allergy considerations
Best Uses
Electroless nickel excels for:
- Sticky formulations (high sugar, polymer content)
- Corrosive products (salts, acids, hygroscopic blends)
- Effervescent tablets where moisture exposure is common
- Quick fixes for moderate sticking issues
Titanium Nitride (TiN) Coating
Description: TiN is a PVD coating famous for its golden color. Applied in a vacuum chamber by vaporizing titanium in a nitrogen atmosphere, creating a thin (~2-5 microns) ceramic layer.
Advantages
TiN’s primary benefits include:
- Exceptional hardness – ~2300 HV (80+ HRC equivalent)
- Wear resistance – Can provide up to 10x longer tool life
- Biocompatibility – Used on medical implants, completely inert
- Low friction – Coefficient of ~0.4, reduces heat buildup
- Visual inspection – Gold color makes wear patterns easily visible
Performance Impact
- Sticking reduction: Good improvement over uncoated tools, though CrN often performs better for pure anti-stick applications
- Wear protection: Excellent for abrasive formulations and high-compression applications
- Corrosion resistance: Superior protection against oxidation and chemical attack
Drawbacks
- Brittleness – Can crack under extreme mechanical stress or impact
- Deposition temperature – Requires ~400°C, which may affect some tool steels
- Not optimal for sticking – While good, chromium-based coatings typically outperform TiN for anti-stick applications
Best Uses
TiN is ideal when tool wear is the primary concern:
- Pressing hard or abrasive granules
- Protecting fine engraving or detailed punch features
- General upgrade from uncoated or chrome-plated tools
- When visual wear indication is valuable
Chromium Nitride (CrN) Coating
Description: CrN is a PVD-applied coating using chromium in a nitrogen atmosphere. Typically silver-gray in color, it has gained a reputation as a superstar for tablet tooling performance.
Advantages
CrN offers exceptional performance across multiple areas:
- Superior hardness – ~2000-2500 HV, comparable to TiN
- Outstanding anti-stick properties – Often considered the best non-proprietary coating for sticking issues
- Excellent corrosion resistance – Dense, nearly pinhole-free coating
- Low internal stress – Can be applied thicker without cracking
- Smooth, dense surface – Discourages powder adhesion
Performance Excellence
Industry experts frequently recommend CrN as the top solution for sticking and picking issues. The coating creates a very smooth, low-friction surface with different surface energy that seems to discourage powder adhesion. Many manufacturers report dramatic reductions in sticking after switching to CrN-coated tooling.
Real-World Impact
- Wear resistance: Comparable to TiN with superior sliding contact properties
- Sticking prevention: Often eliminates frequent cleaning stops
- Durability: Tools maintain performance through millions of cycles
- Cost-effectiveness: Excellent price-to-performance ratio
Best Uses
CrN excels in:
- High-speed, high-volume production where sticking occurs
- Formulations with high binder content (PVP, gums)
- Products prone to picking (logo or text transfer)
- Moisture-sensitive formulations
- Long production campaigns requiring maximum uptime
Multi-Layer Chromium Nitride (MCrN)
Description: MCrN applies multiple layers of chromium nitride to create an almost pore-free surface with enhanced properties. Also called duplex CrN, it appears silver-black or dark gray.
Advantages
The layering approach provides:
- Virtually zero porosity – Second layer covers any defects in the first
- Enhanced durability – Multiple tough layers resist abrasive wear
- Superior corrosion protection – No pathways for corrosives to reach steel
- Increased thickness – Can be applied thicker without stress cracking
- Ultimate smoothness – Pore-free surface minimizes sticking sites
Performance Benefits
- Abrasion resistance: Ideal for mineral-filled or gritty formulations
- Extended campaigns: Perfect for long production runs
- Stress distribution: Alternating layers help prevent crack propagation
Best Uses
MCrN is the premium choice for:
- Highly abrasive formulations (calcium carbonate, minerals)
- Extended production campaigns (millions of tablets)
- Maximum corrosion protection requirements
- Multi-tip tooling where failure costs are high
- Critical applications requiring the ultimate in coating performance
PVD “Chrome” (Advanced Chromium Coatings)
Description: Advanced chromium-based coatings applied via PVD that deliver chrome plating benefits without the drawbacks. These proprietary coatings achieve ultra-smooth, anti-stick surfaces.
Advantages
- Mirror-smooth finish – Extremely fine, homogeneous microstructure
- Superior anti-stick – Some formulations outperform even CrN
- No plating defects – Vacuum process eliminates micro-cracks
- Environmental safety – No toxic plating baths
- Thin application – Doesn’t affect tight tolerances
Specialized Performance
Recent developments include “super smooth” chromium nitride variants that have shown double the anti-stick resistance compared to standard CrN coatings. These represent the cutting edge of anti-sticking technology.
Best Uses
- Extreme sticking problems that other coatings haven’t solved
- Oily or waxy formulations (supplement tablets with extracts)
- Polymer-coated products that tend to smear
- Environmental compliance requirements avoiding chrome plating
How to Choose the Right Coating
Selecting the optimal coating depends on your specific challenges:
1. Identify Your Primary Issue
For Sticking/Picking:
- First choice: Chromium nitride (CrN)
- Alternatives: PVD chrome coatings, Nickel/PTFE
For Excessive Wear:
- First choice: Titanium nitride (TiN) or Multi-layer CrN
- Consider: Tool steel upgrade plus coating
For Corrosion:
- First choice: Electroless nickel or CrN
- Note: Avoid micro-cracked chrome plating
2. Consider Production Scale
- High-volume continuous: Premium coatings (CrN, MCrN) pay off through reduced downtime
- R&D/small batches: Mid-level coatings may be sufficient
- Calculate ROI: Coating cost vs. tool replacement frequency
3. Evaluate Compatibility
- Ensure coating can be applied to your tool steel
- Consider punch designs and engraving details
- Verify regulatory compliance (FDA, USP standards)
4. Budget vs. Benefit Analysis
While premium coatings cost more upfront, consider:
- Extended tool life (often 5-10x longer)
- Reduced downtime for cleaning/maintenance
- Lower reject rates from defects
- Decreased tool replacement costs
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Will coatings contaminate our tablets?
A: When properly applied, these coatings are inert and non-shedding. They’re used on medical implants and surgical instruments. All recommended coatings are FDA-compliant for pharmaceutical use when applied by qualified vendors.
Q: How long do coated tools last?
A: PVD coatings (TiN, CrN) can extend tool life by 5-10x or more. For example, punches might go from 1 million to 10 million tablets before requiring maintenance. Results vary by formulation hardness and press settings.
Q: Can I recoat worn punches?
A: Yes, punches can typically be stripped and recoated 1-2 times. This is often more cost-effective than purchasing new tooling, provided the base steel is still in good condition.
Q: Do coated tools require special maintenance?
A: Coated tools should be handled carefully to avoid chipping. Use non-abrasive cleaning methods, avoid metal-to-metal contact, and inspect regularly for wear. They often require less maintenance overall due to their superior properties.
Q: What’s the cost difference between coatings?
A: Hard chrome is cheapest, electroless nickel is moderate cost, and PVD coatings (TiN, CrN) are more expensive but offer the best ROI through extended life and improved performance.
Conclusion: Optimize Your Tablet Production
Tool coatings represent a smart investment for pharmaceutical manufacturers aiming to reduce downtime, reject rates, and tooling costs. Each coating has its niche:
- Hard chrome for basic, budget protection
- Electroless nickel for sticky, corrosive formulations
- TiN for superior wear resistance
- CrN for the best anti-stick performance
- MCrN for extreme conditions
- PVD chrome for specialized anti-stick needs
The right coating strategy can transform your tablet production – imagine reducing tool changes by 80% while eliminating mid-run cleaning stops. Many companies have solved persistent sticking issues overnight by switching to appropriate coatings.
Ready to optimize your tooling performance? Don’t let sticking or wear slow down your production. The investment in quality coatings pays for itself through improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Need personalized guidance for your specific formulation challenges? Contact our team for a free tooling consultation and discover which coating will deliver the best results for your tablet production.